Wednesday, July 6, 2011
2SAS #13-25, p. 131-132
13) Give another term for each of these features of the periodic table:
a. row.
b. column.
a. A horizontal row is also a period, with elements listed in order of increasing atomic numbers.
b. A vertical column is a group, that contains elements with similar properties.
14) Give the names and symbols of two elements other than lithium in the alkali metal family.
Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K).
15) Consider the noble gas family:
a. Where are noble gases located on the periodic table?
b. Name one physical property that noble gases share.
c. Name one chemical property that noble gases share.
a. The noble gases are located on the far right side of the periodic table.
b. Noble gases are unreactive.
c. Noble gases are chemically inert.
16) Given a periodic table and the formulas BeCl2 and AlN, predict the formula for a compound containing
a. Mg and F.
b. Ga and P.
a. MgF2
b. GaP
17) The melting points of sodium (Na) and rubidium (Rb) are 98°C and 39°C respectively. Estimate the melting point of potassium (K).
Potassium is right between sodium and rubidium on the periodic table:
98+39=137
137/2=68.5
Melting point: 68.5°C.
18) Would you expect the boiling point of chlorine to be higher or lower than that of iodine? Explain.
I would expect the boiling point of chlorine to be lower than that of iodine. From what I have observed, I believe that elements with higher atomic weights have higher boiling points than those with lower atomic weights. Chlorine has a lower atomic weight (35.45) than iodine (126.90), so, chlorine must have a lower boiling point.
19) Copy and complete the following table for each electrically neutral atom.
Completed chart:
20) Using Figure 2.11 (page 121) as a model, illustrate the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of
a. beryllium.
b. nitrogen.
c. neon.
a. 4 protons, 4 or 5 neutrons, 4 electrons.
b. 7 protons, 7 or 8 neutrons, 7 electrons.
c. 10 protons, 10 or 11 neutrons, 10 electrons.
21) A student is asked to explain the formation of a lead (II) ion (Pb^2+) from an electrically neutral lead atom (Pb). The student says the a lead atom must have gained two protons to make the ion. How would you correct this student's mistaken explanation?
Although protons are positive, when an atom forms an ion, it either loses or gains electrons. Since a lead ion with a 2+ charge was formed, the atom must have lost two electrons; when electrons are lost, there are more protons remaining in the atom, resulting in the formation of cations, positively charged ions.
22) Refer to the table provided for Question 19:
a. Calculate the mass number for each element in the table.
b. Which element has two isotopes in the table?
a.
Carbon: 6+6=12, or 6+7=13; 12 or 13
Calcium: 20+21=41; 41
Platinum: 78+117=195; 195
Uranium: 92+146=238; 238
b. Carbon has two isotopes in the table.
23) A scientist announces the discovery of a new element. The only characteristic given in the report is the element's mass number of 266. Is this information sufficient, by itself, to justify the claim of the discovery of a new element? Explain.
No, the discovery of a new element would not be justified by only its mass number. It would be more helpful to know either the atomic weight or atomic number in order to be able estimate physical and chemical properties of the element and its probable spot on the periodic table. An element's mass number does not provide enough information to justify its existence.
24) How does the mass of an electron compare to the masses of a proton and a neutron?
The mass of an electron is about 1/2000 the mass of a proton or a neutron. Because of its minuscule weight, it is insignificant, and not used to calculate the mass number of an atom.
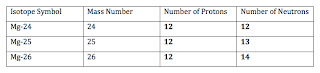
25) How many protons and neutrons are needed for each magnesium isotope in this table?
Completed Chart:
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)




No comments:
Post a Comment